The Secret World of Axolotls: Aquatic Marvels Unveiled
In the depths of Mexico's ancient lakes, a captivating creature has captured the hearts of scientists and pet enthusiasts alike. The axolotl, with its perpetual smile and remarkable regenerative abilities, stands as a testament to nature's ingenuity. This article delves into the fascinating world of these aquatic salamanders, exploring their unique traits, conservation status, and rising popularity as exotic pets.
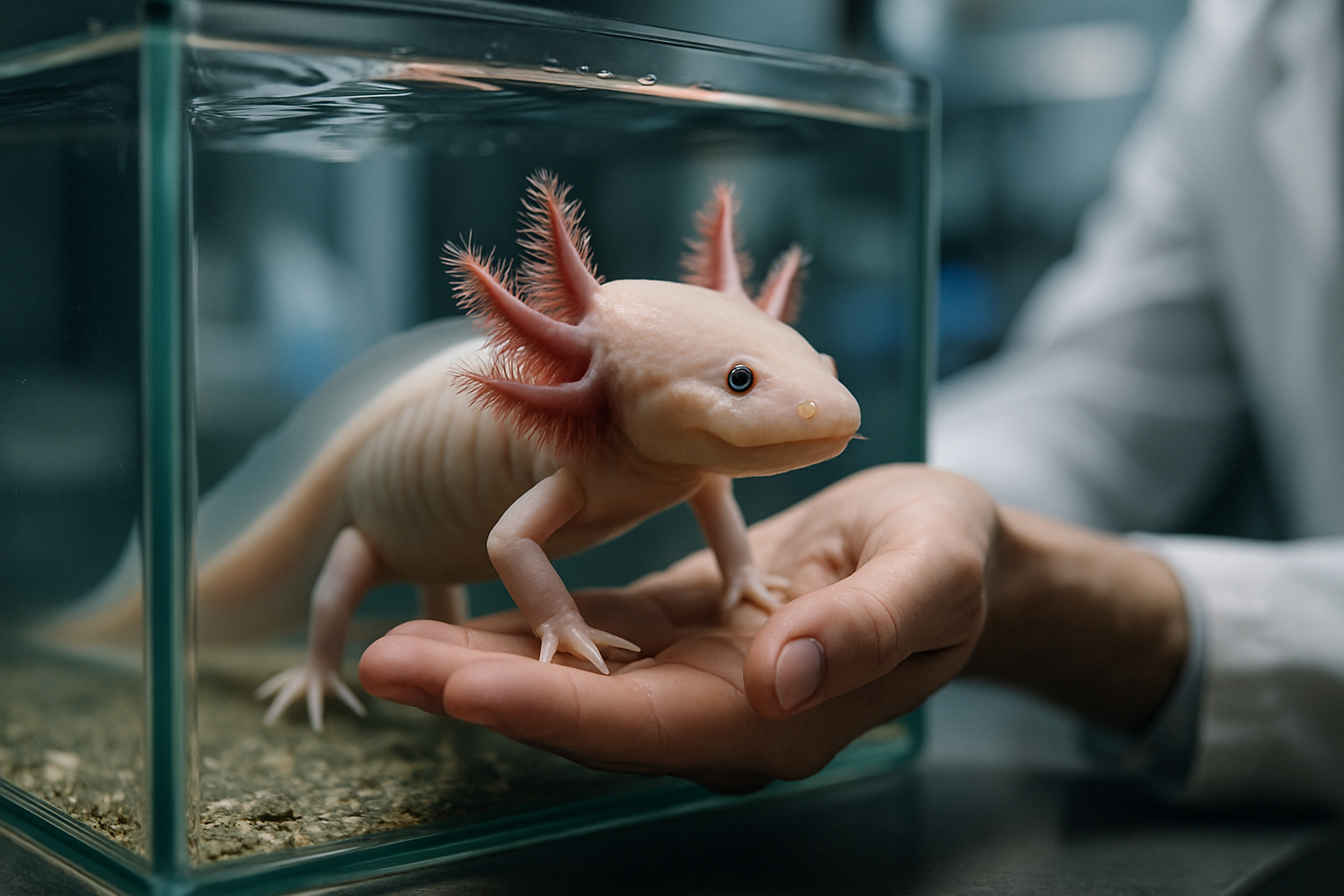

A Glimpse into Axolotl Biology
Axolotls possess a unique set of biological characteristics that set them apart from other salamanders. Unlike most amphibians, axolotls exhibit neoteny, retaining juvenile features throughout their lives. This means they never undergo metamorphosis to become terrestrial adults, instead remaining aquatic and retaining their iconic external gills. These feathery appendages, resembling a crown around their heads, serve as their primary means of oxygen absorption.
Another remarkable feature of axolotls is their extraordinary regenerative capabilities. They can regrow not only limbs and tails but also parts of their brain, heart, and other vital organs. This regenerative prowess has made them invaluable in medical research, potentially holding the key to unlocking similar abilities in humans.
Conservation Challenges and Efforts
In their native habitat, axolotls face numerous threats that have led to a drastic decline in wild populations. Urban expansion, water pollution, and the introduction of invasive species have all contributed to the axolotl’s critically endangered status. The Mexican government and conservation organizations have implemented various measures to protect these unique creatures, including habitat restoration projects and captive breeding programs.
One innovative conservation approach involves the creation of artificial axolotl habitats within Mexico City’s remaining canal systems. These protected areas aim to provide a safe haven for axolotls while also serving as educational sites for the public. Additionally, international efforts to maintain genetically diverse captive populations have been crucial in preserving the species for future reintroduction efforts.
The Rise of Axolotls as Exotic Pets
In recent years, axolotls have gained significant popularity as exotic pets, captivating enthusiasts with their unique appearance and relatively low maintenance requirements. This trend has led to an increase in axolotl breeding and a growing market for specialized care products. The estimated price range for a pet axolotl can vary widely, typically ranging from $20 to $70, depending on factors such as color morph and breeder reputation.
The axolotl pet trade has had both positive and negative impacts on conservation efforts. While it has raised awareness about these fascinating creatures, it has also led to concerns about the genetic diversity of captive populations and the potential for illegal wild collection. Responsible pet ownership and support for ethical breeding practices are crucial for balancing the benefits of axolotl keeping with conservation needs.
Axolotl Care: Challenges and Best Practices
Keeping axolotls as pets requires specialized knowledge and dedication. These aquatic salamanders have specific environmental needs that must be met to ensure their health and well-being. Water quality is paramount, with axolotls requiring cool, clean water with minimal chlorine and other contaminants. A properly cycled aquarium with efficient filtration is essential for maintaining optimal water conditions.
Diet is another crucial aspect of axolotl care. In captivity, they thrive on a varied diet of live and frozen foods, including earthworms, bloodworms, and small fish. It’s important to avoid overfeeding and to ensure that food items are appropriately sized to prevent choking hazards.
One of the most challenging aspects of axolotl care is managing their temperature requirements. Unlike many aquarium inhabitants, axolotls prefer cooler water temperatures, typically between 60°F and 64°F (15°C to 18°C). Maintaining these lower temperatures often requires the use of chillers or creative cooling solutions, especially in warmer climates.
The Future of Axolotl Research and Conservation
As interest in axolotls continues to grow, so does the potential for groundbreaking research and conservation initiatives. Scientists are delving deeper into the genetic mechanisms behind axolotl regeneration, hoping to unlock secrets that could revolutionize regenerative medicine. Recent advancements in gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, have opened new avenues for studying axolotl genetics and potentially applying their regenerative abilities to human health.
Conservation efforts are also evolving, with a focus on holistic approaches that consider the entire ecosystem. Researchers are exploring the use of environmental DNA (eDNA) techniques to monitor wild axolotl populations more effectively, allowing for non-invasive population assessments in their murky natural habitats.
The axolotl’s journey from an obscure Mexican salamander to a global icon of regeneration and conservation showcases the interconnectedness of scientific research, pet keeping, and wildlife preservation. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of these remarkable creatures, it becomes increasingly clear that the fate of axolotls is inextricably linked to our own. By fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for these aquatic marvels, we can work towards a future where axolotls thrive both in the wild and in our hearts.